Curves
The default building elements are efficient for modeling simple building shapes. To make more complex buildings with curved walls or walls that are slanted in x-, or y-direction you can use the power of solid modeling. Complex models are made by adding, subtracting or uniting basic shapes like cylinders, spheres, and curved surfaces.
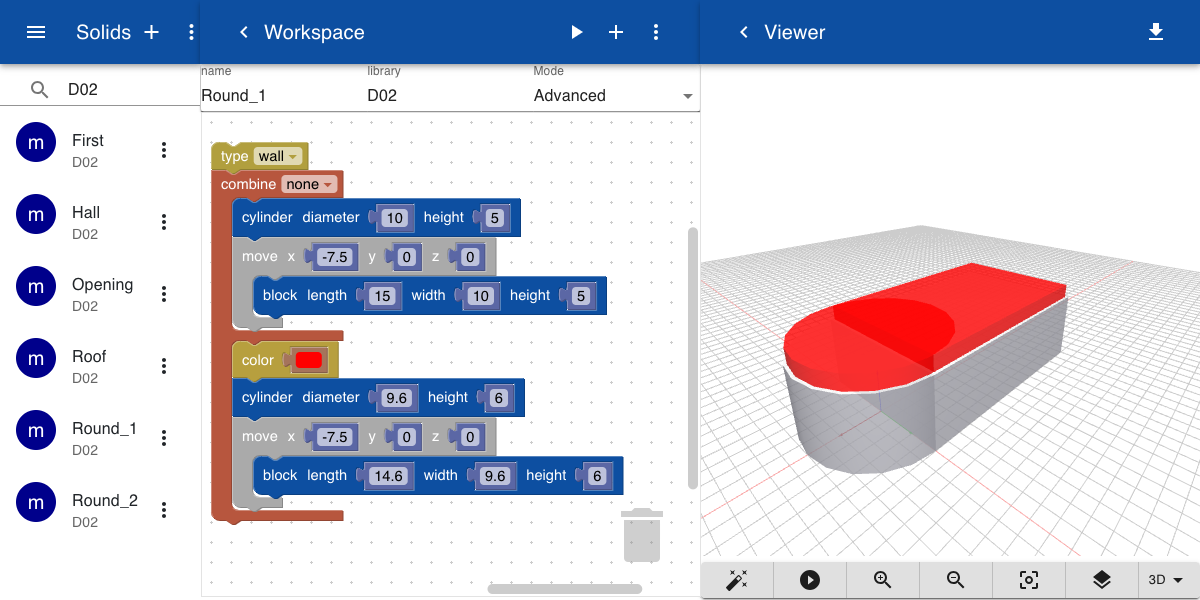
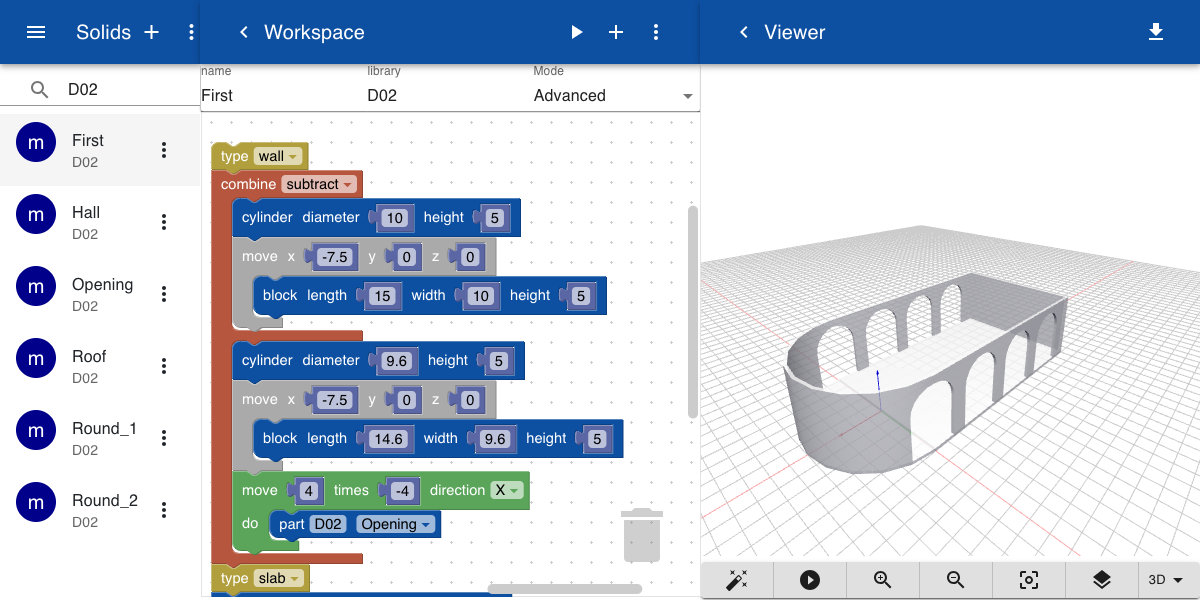
In the example below we create a semi-circular area by adding a cylinder and a block, and subtracting a cylinder and a block with a smaller size. For this, we use the operation Combine.
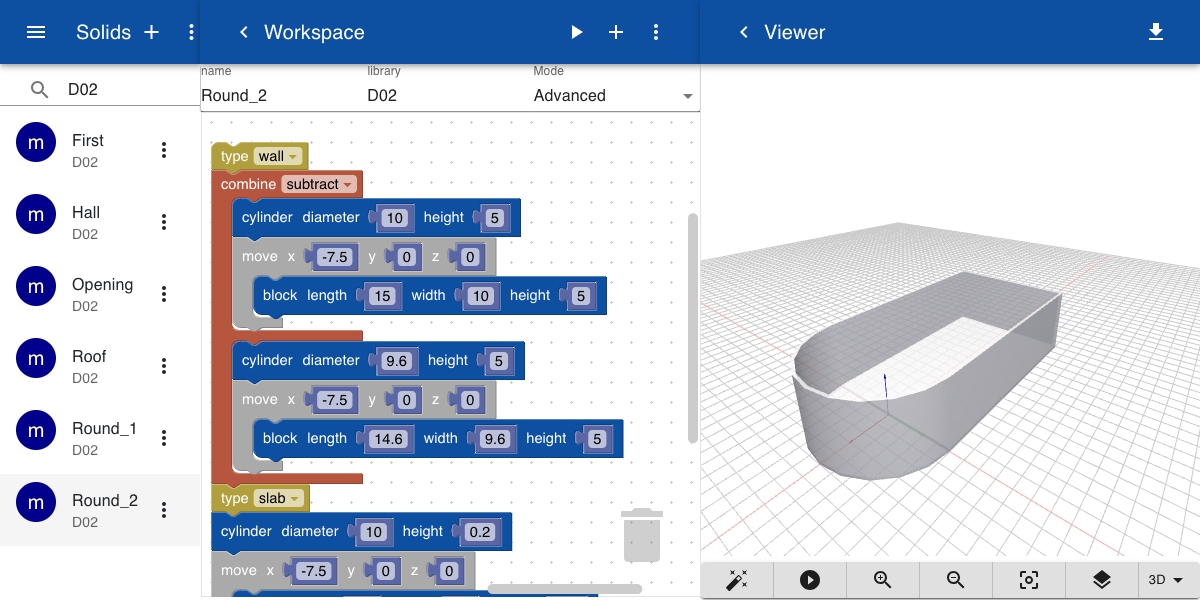
If we change the Combine operation from None to Substract a hollow shape is formed. We now add the Type block to indicate that this object is a wall. We also added another cylinder and a block with a height of 0.2 meters to indicate that this is a Slab. Alternatively, we could have added a move transformation of 0.2 in the z-direction of the block and the cylinder in the example above. The floor then would be a part of the wall.
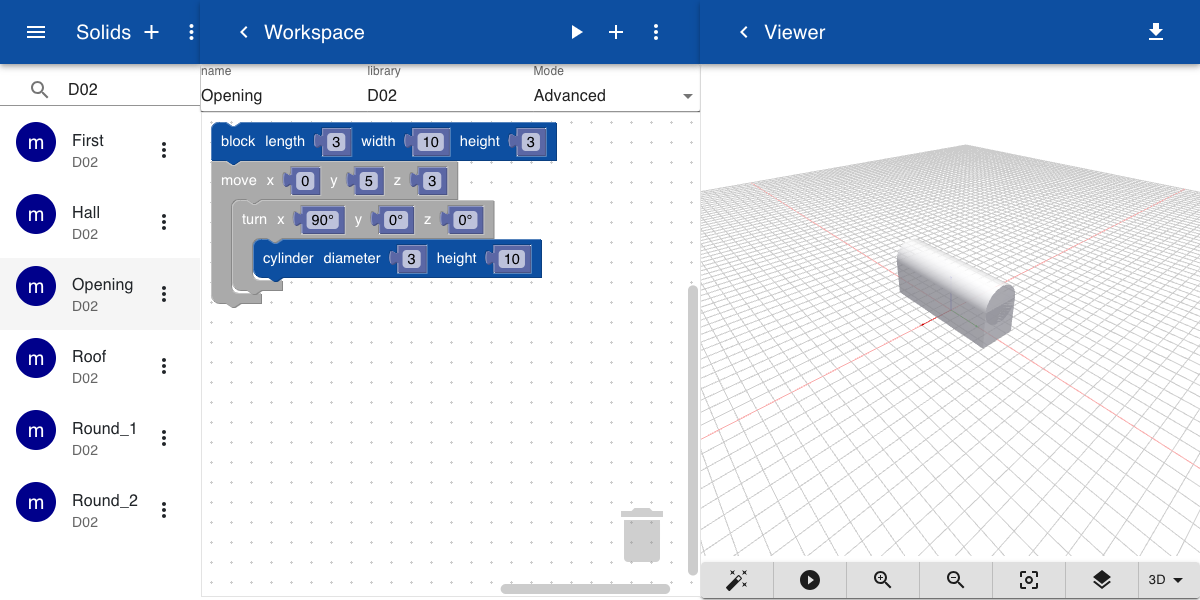
To cut rounded openings in the wall we create a new object that is big enough to cut through both walls. We save this object as Openings.
The openings are now included in the Combine block by adding a Part block and selecting the object Openings. We have also added a repeat block to move the part 4 times in the x-direction.
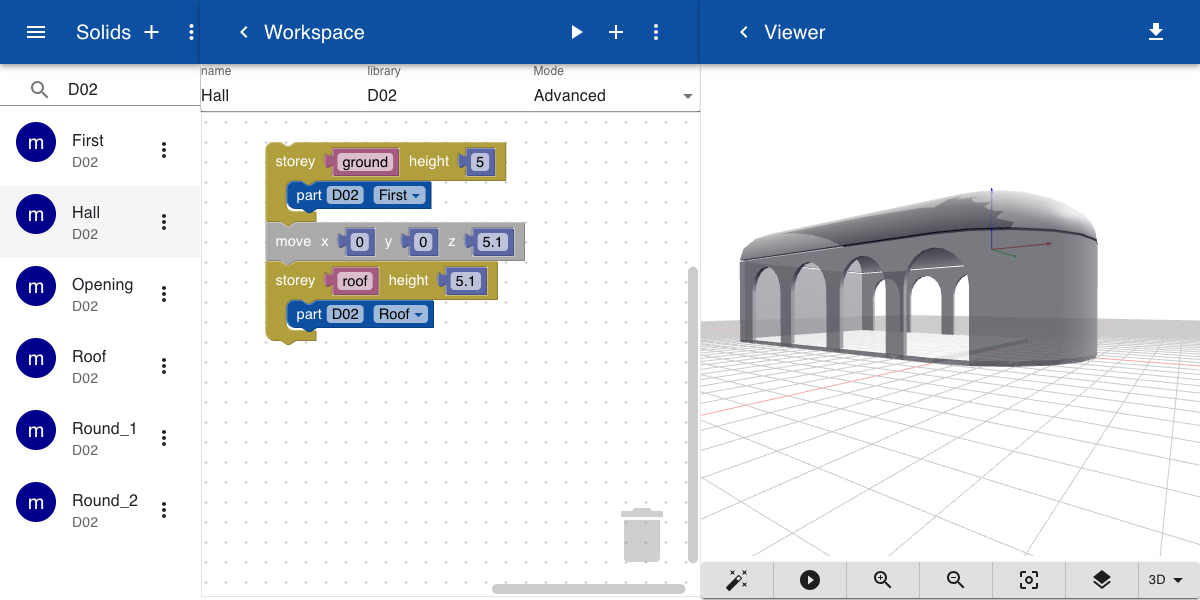
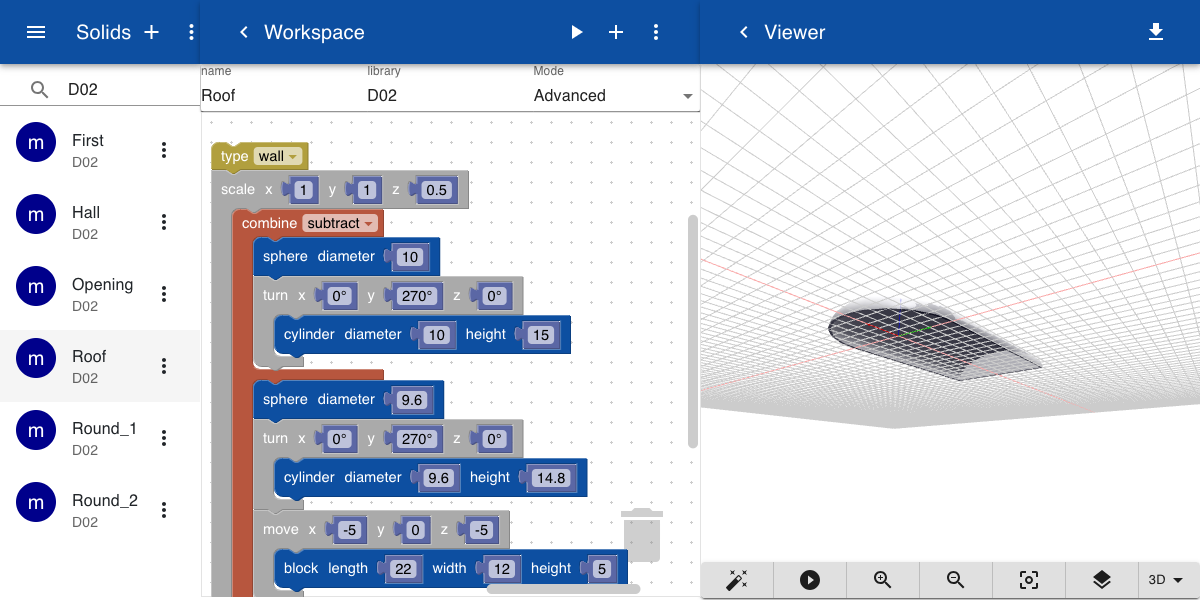
A doubly-curved hollow roof is constructed by subtracting a cylinder and a sphere from a slightly larger cylinder and sphere. The roof is flattened by applying a Scale operation in the z-direction.
Finally, the two elements are combined into a building with two storeys. This will allow the user to view the building without the roof in the viewer by turning off the Roof.