Data exchange
Data is acquired by people, sensors, and systems. The data is analyzed and visualized in 2D dashboards and 3D models. Custom rules defined with visual programming can be used to update the physical model through actuators connected to the internet.
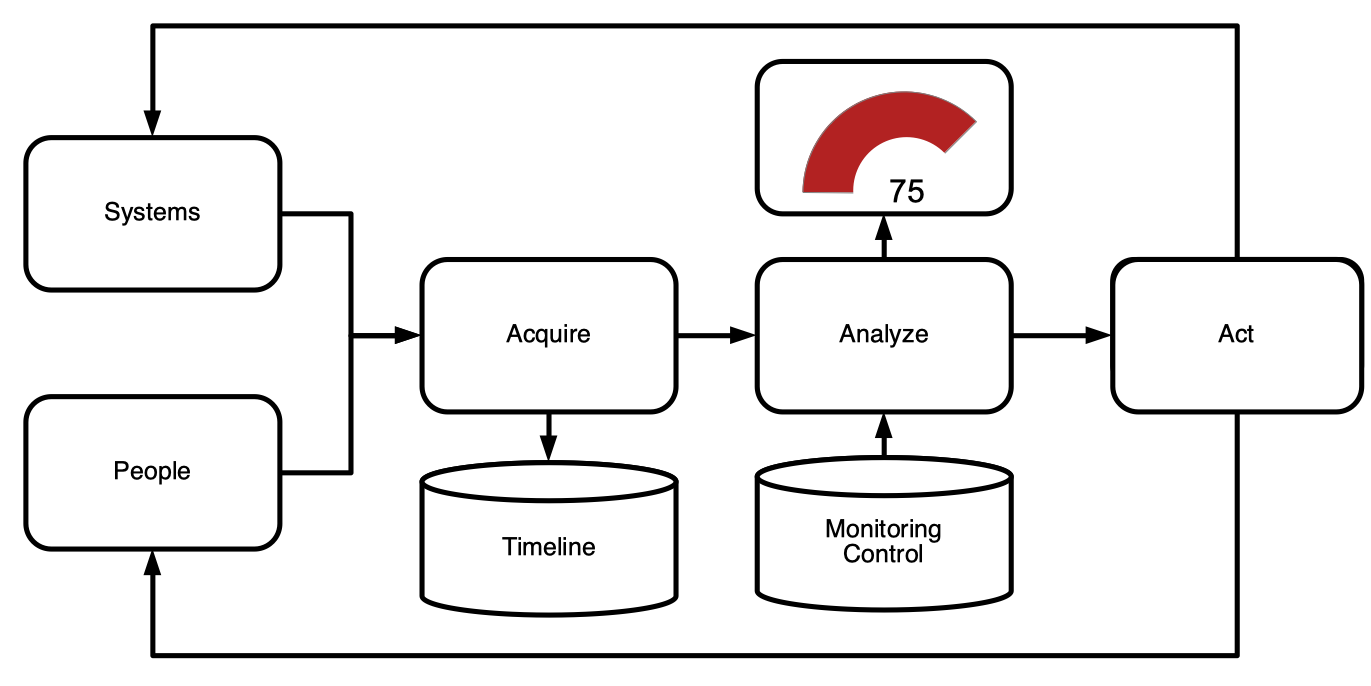
Acquire
Low-cost devices connected to the internet can push information about temperature, humidity or pressure. They are like the eyes and ears of a living creature. Information can also be pulled from other systems such as for weather forecasting, enterprise resource management (ERP) or customer relationship managment (CRM). Similarly to nerves in a living creature, signals can be transported over wired connections, WIFI, bluetooth, 4G, Zwave or ZigBee. Data formats includes text messages, structured data in JSON format, images or documents. In case there are no sensors, people may manually gather the data by completing checklists and inspections. Data may also acquired by asking people for opinions via surveys or assessing their qualifications with a test or quiz. The acquired data is converted into a common format for long term storage in memory. This memory may help to detect trends and make better decisions in the future.
Analyze
The analysis part can be compared to the autonomous nerve system and brain of living creatures. They sense that pressure is too high or temperature is too low or recognize danger based on past experience. In buildings information from temperature sensors and presence detection can be combined to analyze whether or not the temperature is too low. In enterprise systems the rate of sales per month can be used to forecast and project, taking into account various parameters such as seasonality and marketing investments. Visualization of data in dashboard, time-charts, maps or 3D digital models helps to understand how parameters change per location and over time. The availability of open source machine learning technology facilitates automatic trend analysis and find relationships between input parameters.
Act
The basis for acting is a set of rules that describe the desired state of the system. When dealing with systems, acting may involve the activation of a control such as a thermostat, valve or motor. When dealing with people acting may involve sending a notification about anomalies or non-compliance with the request to take action. Sometimes a combination of acting and notfication is used. For example, with self-driving cars the car should remain in the lane with a constant speed. When a deviation from the desired state is detected the car takes action by sending a signal to a motor that controls the steering system. However, when the car does not know how to handle a situation a notification is sent to the driver to take immediate action. In biology, the autonomous nervous system immediately triggers a muscle to retract your hand when the surface is too hot. When the body can not automatically solve the problem is sends a message like a pain signal to force you to slow down and inspect the problem.